Water activities—from swimming and boating to fishing and diving—are enjoyed by millions of people worldwide. While these activities offer recreation, fitness, and stress relief, they also carry risks. Drowning remains one of the leading causes of unintentional injury-related deaths globally. The solution lies not only in having lifeguards and safety personnel on duty but also in ensuring that communities, families, and individuals have access to water safety training.
What is Water Safety Training?
Water Safety Training is an educational and practical program designed to equip individuals with the knowledge and skills needed to prevent, recognize, and respond to water-related emergencies. Training can be offered through schools, community centers, aquatic facilities, and organizations such as the American Lifeguard Association, Royal Life Saving Society. It is aimed not only at lifeguards but also at parents, teachers, and recreational swimmers.
Core Components of Water Safety Training
Basic Swimming and Survival Skills
Trainees learn essential swimming techniques, floating, treading water, and survival strokes. Even minimal swimming ability can significantly improve a person’s chances of survival if they fall into water unexpectedly.Recognizing Hazards
Instruction covers environmental risks such as rip currents, sudden drop-offs, weather changes, and unsafe pool behaviors. Awareness is the first line of defense in preventing accidents.Rescue Techniques
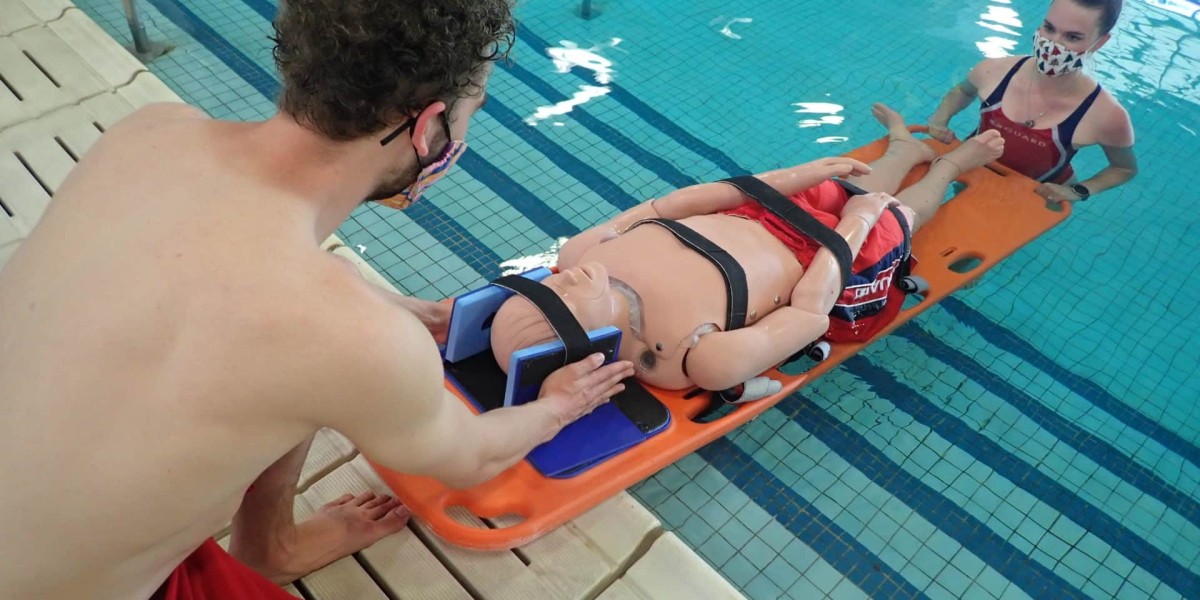
Water safety courses emphasize safe rescues without putting the rescuer at risk. Techniques include reaching assists, throwing flotation devices, and in-water approaches for trained individuals.CPR, AED, and First Aid
Since drowning and near-drowning incidents often lead to cardiac or respiratory emergencies, participants learn cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), how to use automated external defibrillators (AEDs), and how to provide basic first aid until professional help arrives.Emergency Preparedness
Trainees practice responding calmly to emergencies, calling for help, and coordinating with others. Preparedness reduces panic and increases effectiveness during real incidents.
Why Water Safety Training Matters
Prevention of Accidents: The majority of drownings are preventable. Training instills habits such as always swimming with a buddy, supervising children, and using life jackets in open water.
Community Confidence: Facilities with trained staff and communities with safety-conscious residents create safer environments, attracting more people to participate in aquatic activities.
Life-Saving Impact: Even a bystander who has undergone basic water safety training can save a life while waiting for professional rescuers.
Who Should Take Water Safety Training?
Everyone benefits from water safety education. Parents of young children, teachers, camp counselors, recreational swimmers, and boating enthusiasts should consider training. Lifeguards and aquatic staff undergo more advanced, specialized courses, but even casual swimmers can gain life-saving knowledge through community-level programs.
Final thought
Water Safety Training is more than just a course—it is an investment in saving lives. By teaching people how to swim, recognize hazards, respond to emergencies, and administer CPR, these programs empower communities to reduce preventable tragedies. Whether at a pool, a beach, or a lake, safety must always come first. With proper training, individuals gain the confidence and skills to enjoy aquatic activities responsibly while protecting themselves and others.